JILPT Research Report No.184
Collective Agreement Systems in Modern Industrialized Nations:
Summary and Observations
May 31, 2016
Summary
Research Objective
To clarify the current status of collective agreement systems in modern industrialized nations (Germany, France and Sweden) and the realities of norm setting based on these systems, and to highlight similarities and differences between the three countries by comparing their respective systems.
Research Method
Literature surveys
Local interview surveys
Main Findings
This Research clarified similarities and differences between collective agreement systems in each country and the realities of norm setting based on these systems, as follows.
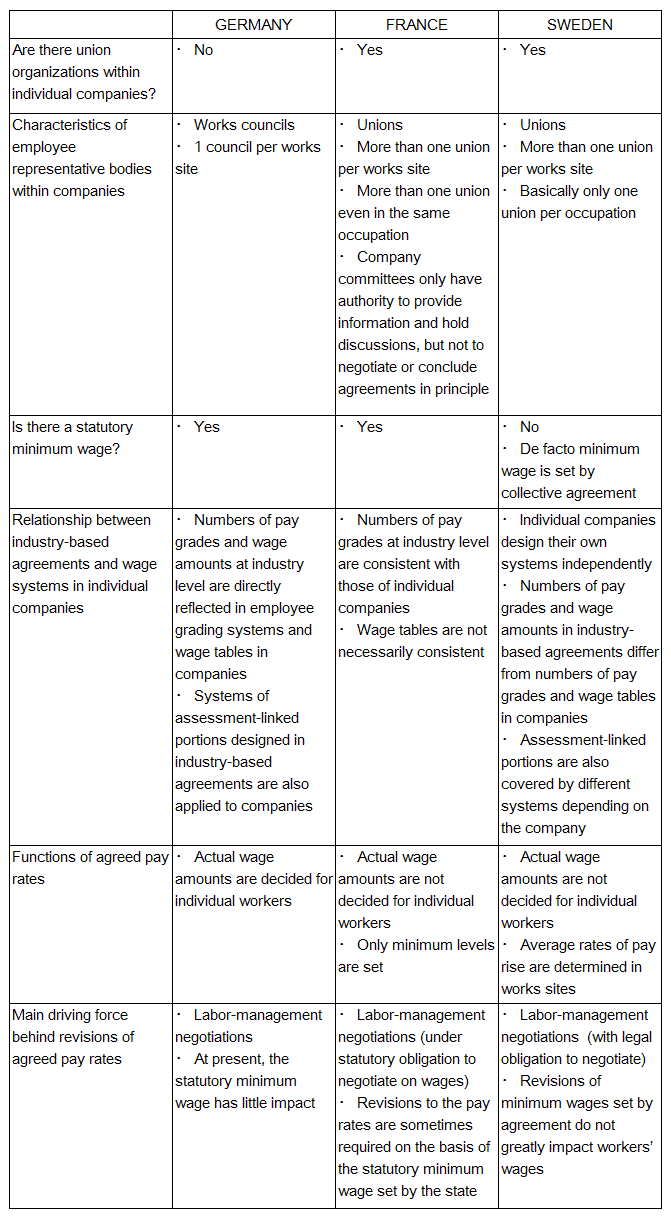
Passive state involvement type (Germany, Sweden)
A number of similarities were found between Germany and Sweden. One of them was that, compared to France, the involvement of the state is limited. Another was that industry-based agreements have significance over and above that of determining minimum standards of working conditions. In Germany, pay grades determined in industry-based agreements are applied directly as company pay grades. In Sweden, industry-based agreements set rules for average pay rise rates in work sites, in addition to minimum wages. In this way, industry-based agreements have significance over and above that of merely setting minimum standards in companies’ personnel and wage systems.
However, the two countries differ in the level at which working conditions are mainly decided. This is done at industry level in Germany and at company level in Sweden. The specific contents of wage-related agreements vividly illustrate this point. In Sweden, the number of pay grades and the respective pay rates are decided at company level. In Germany, they are decided at industry level. This also applies to merit pay systems. In Sweden, this aspect of pay is decided at company level. In Germany, again, it is decided at industry level.
Even so, similarities are thought to lie at the heart of these differences. That is to say, in both countries the main stage for deciding working conditions coincides with the lowest level at which labor unions can be organized.
Active state involvement type (France)
In France, on the other hand, industry-based agreements determine minimum levels of working conditions. In that sense, industry-based agreements cannot necessarily have provisions for pay grades of individual companies or pay rates for each grade. France differs from Germany and Sweden in this respect.
Also, the role played by the state in setting these norms is more significant than in the other two countries. The characteristics of the French system are thought to be further underlined by the fact that minimum wage revisions seen in recent years sometimes impact revisions of agreed pay rates. Moreover, the low level of union involvement in evaluating workers, compared to the other two countries, might suggest a low interest in maintaining the unity of the unions.
Based on the above, the characteristics of the three countries can be summarized as shown in the table below.
Figure: Characteristics of the three countries
Policy Contribution
The published results are due to be used as Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare data in various government meetings.
Contents (available only in Japanese)
- JILPT Research Report No.184 / Whole text (PDF: 5.8MB)
If it takes too long to download the whole text, please access each file separately.
Research Category
Project Research: “Survey Research on Systems for Deciding Working Conditions Centered on Labor Relations”
Subtheme: “Research Project on Directions for Collective Labor Relations in Connection with the Establishment of Norms”
Research Period
FY2015
Author
- Itaru NISHIMURA
- Researcher, Department of Human Resource Management
- Yota YAMAMOTO
- Researcher, Department of Industrial Relations
- Ryo HOSOKAWA
- Researcher, Department of Industrial Relations
Catergory
Employment / Unemployment, Labor laws / Working rules, Industrial relations, Working conditions / Work environment
JILPT Research Report at a Glance
| To view PDF files, you will need Adobe Acrobat Reader Software installed on your computer.The Adobe Acrobat Reader can be downloaded from this banner. |

